Master of Science in Cyber Security
Digital Forensics Specialization
New Term Begins
5th Jan, 2026
Program Duration
2 Years
Number of Courses
12 (36 Semester Credits)
Learning Format
Online / Hands-On
Certifications Included
Up to 3
Achieve a Master’s Degree in Cyber Security and Lead as a Digital Forensics Expert
With a curriculum that goes beyond traditional academic frameworks, EC-Council University integrates practical training with industry-recognized certifications, such as the Certified Ethical Hacker (CEH), Computer Hacking Forensic Investigator (CHFI), and Certified Network Defender (CND). This approach equips you with tangible skills and a competitive edge, enabling you to tackle cybersecurity challenges with confidence.
This advanced masters in digital forensics prepares you for 20+ cybersecurity roles, providing you expertise in critical aspects of digital forensics like investigating network intrusions, mobile forensics, cyber law, data recovery, digital evidence preservation, and more.
Master In-Demand Technical Expertise
Build Practical, Hands-on Skills
Advance with Management & Soft Skills Mastery
Admission Inquiry
Talk to Our Admission Counselor —we’re here to help you use your VA benefits
"*" indicates required fields
World-Class Cyber Security Education Focused on Digital Forensics
Discover the True University Experience with ECCU
Gain In-Demand Skills to Advance as a Digital Forensics Specialist
Network Security
Develop your expertise in network protocols, configurations, and security measures, essential for various cyber security job roles.
Digital Evidence
Master the methods for acquiring, preserving, analyzing, and presenting electronic evidence in a court of law.
Track the Cyber Trail
Become adept at investigating network intrusions, uncovering digital footprints left by cyber criminals, and piecing together cyber-attack timelines.
Mobile Forensics
Enhance your proficiency in mobile forensics by extracting and analyzing data from mobile devices to uncover crucial digital evidence.
Computer Forensics
Develop computer forensic skills and knowledge that are highly sought-after by government agencies and private sector organizations.
Soft Skills
Augment your technical skill set with improved communication, leadership, decision-making, problem-solving, and critical thinking capabilities.
Master of Science in Cyber Security - Digital Forensics Specialization
ECCU’s online forensics degree consists of 8 foundational courses, 3 specialized courses, and 1 Capstone project.
Foundational Courses
ECCU 505Introduction to Research and Writing (3 Credit Hours)
This course introduces you to basic English writing skills and research methods, including APA-style writing, citing sources, determining when a website is credible, and using effective business communication.
ECCU 504 Foundations of Organizational Behavior (3 Credit Hours)
This course deals with organizational behavior, allowing you to experience the basic facets of organizational theory and define the skills required to understand and apply the theory to real-world environments. Elements of the course are organizational structure, effective communication, team building, ethics, and project management, as seen through the organizational lens.
ECCU 514 Leadership and Management in Organizations (3 Credit Hours)
This course encompasses an extensive research project about cross-cultural differences in leadership conducted by a group of researchers in 62 countries. It lays a foundation for understanding the process of leadership. The study examines the roles, functions, and impact of global leadership concepts, along with team exercises that simulate the speed at which leaders must act. Research and views into how most cultures respond to this management area are also provided.
ECCU 516 The Hacker Mind: Profiling the IT Criminal (3 Credit Hours)
While cyberspace has increased human communication, connectivity, creativity, and capacity, it has also increased crime exponentially in the last decade. This crime aspect is exploited by everyone from hackers in high school to international terrorists. IT criminals threaten businesses, governmental agencies, militaries, and organizations of every kind. This course will survey the spectrum of psychological attributes that make up the profile of IT criminals.
MGMT 502 Business Essentials (3 Credit Hours)
This course provides a comprehensive foundation in business principles, equipping you with essential knowledge and skills applicable across various business environments. You’ll develop a strong understanding of key business concepts by exploring how successful entrepreneurs navigate global competition and evolving market dynamics.
ECCU 500 (CND Certification) Managing Secure Network Systems (3 Credit Hours)
This course evaluates network and IT security issues, designing and implementing successful security policies and firewall strategies, exposing system and network vulnerabilities, and defending against associated threats. Topics include network protocols, network attacks, intrusion detection systems, packet filtering, proxy servers, Bastion hosts and honey pots, hardening routers, hardening security, email security, virtual private networks, and creating fault tolerance.
ECCU 501 (CEH Certification) Ethical Hacking & Countermeasures (3 Credit Hours)
This course focuses on how perimeter defenses work, how intruders escalate privileges, and methods of securing IT systems. Additional topics include intrusion detection, policy creation, social engineering, DoS attacks, buffer overflows, and virus creation.
ECCU 507 Linux Networking and Security (3 Credit Hours)
This course focuses on configuring a secure Linux network using the command line and graphical utilities. Emphasis is placed on file-sharing technologies such as the Network File System, NetWare’s NCP file sharing, and File Transfer Protocols. Additional topics include securing data, user security, file security, and network intrusion detection. You will take on the role of a problem solver and apply the concepts to situations that occur in real-world environments.
Specialized Courses
ECCU 502 (CHFI Certification) Investigating Network Intrusions and Computer Forensics (3 Credit Hours)
This course focuses on cyber-attack prevention, planning, detection, and incident response to counter cybercrime, cyber terrorism, and cyber predators and make them accountable. Additional topics include fundamentals of computer forensics, forensic duplication and analysis, network surveillance, intrusion detection and response, anonymity, computer security policies and guidelines, and case studies.
ECCU 521 Advanced Mobile Forensics and Security (3 Credit Hours)
This course focuses on the intricacies of manual acquisition (physical vs. logical) and advanced analysis using reverse engineering to understand how popular mobile operating systems (OS) are hardened to defend against common attacks and exploits. Topics include mobile forensic challenges and processes, mobile hardware design and architectures, OS architectures, boot processes, file systems, threats and security, evidence acquisition and analysis, application reverse engineering, and mobile forensics reporting and expert testimony.
ECCU 517 Cyber Law (3 Credit Hours)
This course focuses on the legal issues surrounding online criminal conduct and electronic evidence, and the legal ramifications of neglecting trademarks, copyrights, patents, and digital rights. Topics include laws, regulations, and international standards; privacy laws governing law enforcement investigations in cyberspace; implications of cybercrimes upon the traditional notions of sovereignty; and current events that affect cyber laws. (ECCU 505 is a prerequisite for this course)
Capstone
ECCU 519 Capstone (3 Credit Hours)
The Capstone is a summative experience, allowing you to demonstrate all program outcomes by drawing on the knowledge and skills gained throughout the program. You can enroll in the Capstone after successfully completing all core degree requirements, but it must be within six semester credit hours of graduation. You must attain a cumulative grade point average of 3.0 and have the Registrar’s approval to undertake the Capstone.
Invest in Your Cyber Security Career
Your investment includes
- 12 in-depth courses
- Hands-on virtual practice labs
- Digital textbooks & instructional materials
- 360° academic advisory support
- Grammarly Pro subscription
- Industry-recognized certifications
New Term Starts On
January 5th, 2026
$1,620
Cost per Course
$19,440
Total Program Fee
A Degree That Offers Significant Returns on Investment
This digital forensic master’s degree gives you the skills to become a digital forensics investigator and meet the rising demand for experts who defend organizations from cyber threats. You’ll master the essentials of digital forensics and cyber-crime investigation, preparing you to step into high-impact roles that are vital to bringing cyber criminals to justice.
Chart Your Earning Potential
1 in 2 ECCU graduates earn annual salaries of over $100,000 after completing the program.
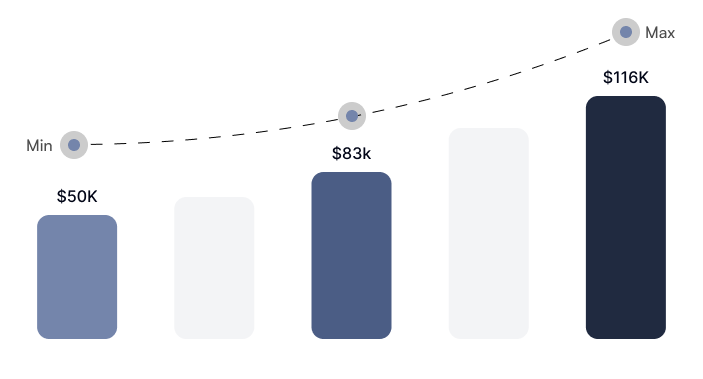
A Digital Forensics Specialist’s Salary Progression
Organizations offer highly competitive salaries and pay hikes to recruit and retain qualified professionals skilled in this vital cyber security discipline.
Watch how Linton Harris transformed his career after graduating from the program.
The Most Affordable Way to Upgrade Your Cyber Security Career
Flexible Payment Options
Financial constraints should not hinder your career aspirations. At EC-Council University, we offer flexible payment plans designed to accommodate your circumstances to support your career development, giving you peace of mind as you study on your own terms. Contact our Finance Team to explore payment solutions tailored to your needs.
Credit Transfer
Leverage your previous academic achievements by transferring credits—such as from an associate degree or other accredited academic programs—toward a master’s degree in cyber security at ECCU, allowing you to fast-track your program. Furthermore, if you hold relevant certifications, you may be eligible to convert this expertise into academic credits.
Scholarship Eligibility
At ECCU, we understand that the cost of higher education can be a challenge for many, which is why we offer a range of scholarships and grants to support your academic journey. For example, the Cyber Security Dean’s Scholarship is offered to deserving students who are academically gifted and dedicated to making their educational experience a successful endeavor.
Prepare for 20+ High-Demand Job Roles
- Digital Forensic Analyst
- Application Security Analyst
- Cyber Crime Investigator
- Information Security Officer
- Cyber Defense Forensics Analyst
- Risk Assessment Specialist
- Incident Response Lead
- Information Assurance Security Officer
- Digital Forensics Specialist
- Mobile Forensics Specialist
- Digital Forensics Engineer
- Forensic Imaging Specialist
- IT Security Specialist
- Law Enforcement Forensics Analyst
- Computer Security Forensic Investigator
- Counterintelligence Forensics Analyst
- Ethical Hacker
- Penetration Tester
- Data Protection & Recovery Specialist
- Security Operations Center (SOC) Analyst
View More…
View Less
Enhance Your Credentials
Immerse Yourself in the Future of Online Learning
Immerse Yourself in the Future of Online Learning
Get the unrestricted advantages of ECCU’s acclaimed Learning Management System (LMS) when you join the Master of Science in Cyber Security program. Our platform offers a fluid and user-friendly UI that seamlessly integrates your library of learning resources and program activities into an engaging virtual classroom that you can access anytime, anywhere. Here’s what you’ll experience:

Live Sessions (30 Mins)

Courseware

Virtual Labs

Quizzes

Discussions

Essential Tools

24x7 Online Library

Capstone Projects

Assignments & Assessments
Accreditations and Recognitions




A Testament to Our
Academic Excellence
ECCU’s online cyber security programs are crafted to empower driven professionals to turn their aspirations into reality and achieve their career dreams.

93%
Employment Rate
ECCU graduates land jobs in leading organizations after completing the program.
82%
Report Career Enhancement
ECCU graduates mention that the programs have had a demonstrable impact on their career growth.
80%
Apply Training at Work
Graduates of ECCU say that the knowledge and skills acquired from the programs are regularly applied at work.
Our Alumni are Making an Impact at the World’s Leading Organizations Across Sectors
Work Alongside Our Alumni in Top Companies
JP Morgan
Pfizer
Apple
Microsoft
Accenture
Amazon
IBM
Lead in Key Industries
Technology
Finance
Healthcare
Education
Manufacturing
Government
Aerospace
Non-Profits
Retail

From Learning to Leading - Your Roadmap to Success
01
Application
Submit the application form along with relevant documents for this online cyber security master’s degree.
02
Evaluation
The Admissions Team evaluates your documents, transcripts, and diplomas to determine eligibility.
03
Registration
Sign the official Student Enrollment Agreement after paying the tuition fee.
04
Orientation
Attend an online orientation session that guides you through the program.
05
Program Completion
Clear the final exams of each course, accompanying assessment, and the Capstone project to acquire credits.
06
Cyber Security Certifications
Earn up to 4 industry-recognized EC-Council certifications.
07
Graduation Ceremony
Graduate with your master’s degree in cybersecurity.
08
Career Guidance
Get expert career guidance and resume-building assistance from ECCU.
Your Admission, Made Simple
Experience a seamless and hassle-free admission process when you enroll in this program. From your first question to your first class, our dedicated Enrollment Advisors are here to guide you every step of the way.
What You’ll Need
Depending on where you’re applying from and your academic background, you might be asked to submit:
Official transcripts of prior education
Valid government identification
Completed application form
Application fee payment
Proof of English language proficiency (if applicable)
Not sure what applies to you? No worries - help is just a click away!
Visit our
Frequently Asked Questions
Q. Is digital forensics a good career choice?
Yes, because digital forensics is a vital part of cyber security. Organizations in both private and government sectors greatly value Digital Forensics Specialists who use their professional skills to prevent and solve cyber attacks and cyber crimes from affecting business.
Q. What program should I choose to become a Digital Forensics Investigator?
If you aspire to become a highly skilled Digital Forensics Investigator, you should enroll in EC-Council University’s masters in digital forensics. This program will equip you with advanced digital forensics skills and knowledge to help your career thrive.
Q. How does digital forensics strengthen an organization’s cyber security protocols?
Using digital forensics, you can discover and trace unauthorized internet access by employees and identify loopholes and vulnerabilities in an organization’s IT network. Digital forensics is also essential in monitoring malware incidents, such as attacks and intrusions. It plays a key role in determining how a breach occurred and how future attacks can be avoided.
Q. How much does a Digital Forensics Specialist earn in a year?
The total yearly salary for Digital Forensics Specialists in the U.S. ranges from $50,000 to $116,500, with an average pay of $83,250.
(*Please Note – Source: ZipRecruiter.com. EC-Council University does not guarantee the salary details mentioned above. The salary will be influenced by factors including but not limited to experience, industry, location, and bonuses.)
Q. Can I pursue this Digital Forensics degree while working a full-time job?
Yes! Most of our students work full-time and manage their studies by learning in the evenings and on weekends. When pursuing ECCU’s digital forensics degree, you should plan to dedicate 10 to 12 hours per week per class. Depending on your schedule, you can take one or two classes per term to balance work and studies effectively.

