In 2026, cyber threats continue to grow in scale, sophistication, and frequency. Technologies like Artificial Intelligence have emerged as one of the most transformative technologies, reshaping the cybersecurity landscape. In the United States, where cyberattacks target everything from critical infrastructure and hospitals to federal agencies, the integration of AI into cybersecurity has made it a strategic necessity rather than a competitive advantage.
Currently, AI isn’t just about enhancing security operations; it is fundamentally changing how defenders detect, predict, and respond to cyber risks. While at the same time, threat actors are leveraging AI to automate attacks, evade detection, and exploit vulnerabilities more rapidly than ever before. This dual nature of AI, its defensive capabilities, and offensive misuse defines the new age cybersecurity landscape.
Today, let us explore how:
- AI in cybersecurity in 2026 shall play a crucial role,
- AI is used as the latest defensive and offensive applications,
- Top AI-powered tools enhance security,
- Businesses can adapt to the evolving cybersecurity tech landscape.
What Is AI in Cybersecurity?
AI in cybersecurity refers to the application of artificial intelligence technologies in enhancing security through Machine Learning, Deep Learning, Natural Language Processing, predictive analytics, and autonomous systems, which help detect, prevent, respond to, and predict cyber threats.
Unlike traditional signature-based or rule-based security systems, AI-powered systems learn from patterns and behaviors, allowing them to adapt more effectively. They analyze massive amounts of data, identify anomalies, recognize new attack patterns, and automate responses in ways human teams alone cannot achieve.
What are the Core Components of AI in Cybersecurity

1. Machine Learning (ML): ML is a sub-technology of AI that helps identify anomalies, classify threats, and improve detection accuracy.
2. Deep Learning (DL): Deep learning is another sub-technology of AI that helps process complex data from network logs, emails, endpoint telemetry, and user behavior.
3. Natural Language Processing (NLP): NLP AI technology assists with analyzing phishing emails and malicious scripts and provides threat intelligence reports.
4. Autonomous Security Systems: It is the process of automating incident response, triage, and containment using AI technology.
AI equips cybersecurity systems with speed, precision, and adaptability—three capabilities that are essential for modern cyber defense.
Importance of AI in Cybersecurity in 2026
In 2026, the US cybersecurity landscape is shaped by rapid digital transformation,
expanded remote work, IoT proliferation, 5G adoption, and AI-powered cybercrime. The threat environment is far more dynamic than it was even just a few years ago.
Why AI Has Become Critical in 2026
1. Threat volume has outpaced human capability
US enterprises generate billions of security events daily, far more than analysts can manually review.
2. Attack sophistication has skyrocketed
AI-driven phishing, polymorphic malware, and automated ransomware have increased the complexity of threat detection, making it more challenging than ever.
3. Faster response times are needed
Unlike earlier, modern attacks are today more sophisticated and swifter, moving from initial compromise to data exfiltration in minutes and not hours.
4. The cybersecurity skills gap persists
AI is widely adopted today to help fill operational gaps within organizations. With this, the expectations of proficient AI professionals have also increased significantly.
5. Zero trust and continuous monitoring rely on automation
AI in cybersecurity serves as the foundation for security, encompassing identity verification, anomaly detection, and resource access decisions.
6. Regulation and compliance pressures are increasing
Considering new regulations and compliance mandates across various sectors, including banking, healthcare, and government, globally, the implementation of advanced threat detection is essential.
Overall, the importance of AI in cybersecurity is driven by necessity. Without AI, modern digital ecosystems are too complex and too fast-moving to be effectively protected.
The AI-Driven Cybersecurity Landscape in 2026
AI in cybersecurity is a technology which is like a double-edged sword that can be used for both offensive and defensive strategies. This redefines the cybersecurity landscape and the use of AI technology in the dynamic field of cybersecurity.
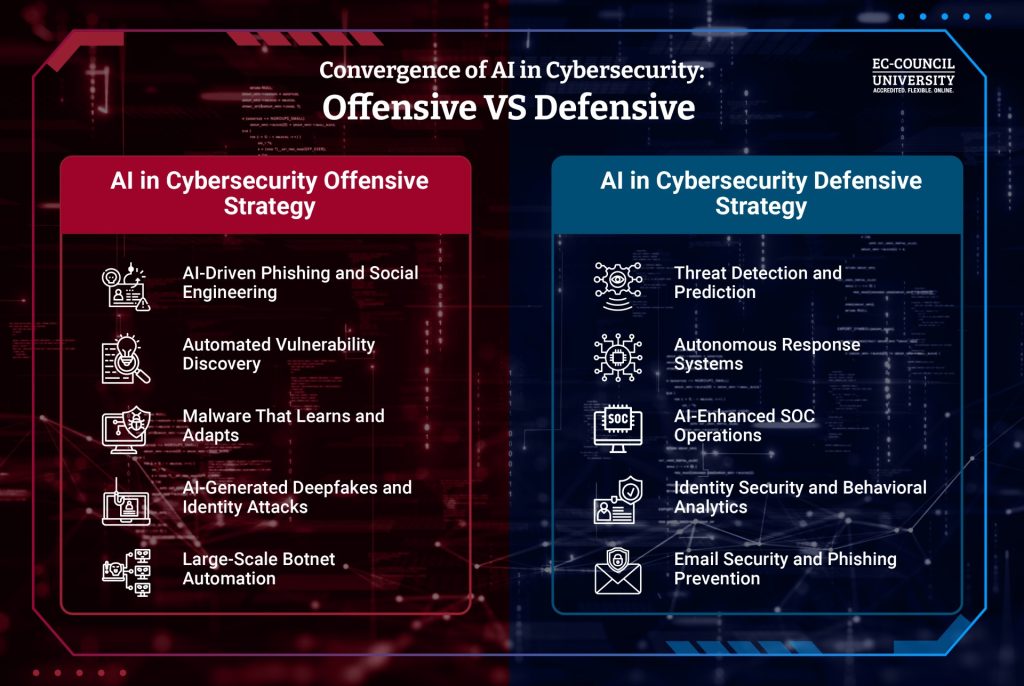
How AI Is Used in Cybercrime in 2026 (Offensive Strategy)
In 2026, AI used for offensive tactics will reach new heights, making cybercrime faster, cheaper, and more accessible. Just as defenders leverage AI, cybercriminals are also weaponizing the technology to create scalable, highly sophisticated, and effective cyberattacks.
Keyways Attackers Use AI in 2026
1. AI-Driven Phishing and Social Engineering
The success rates of cyberattacks have significantly increased as AI makes phishing nearly indistinguishable from legitimate communication. AI technology is used by attackers to
- Deepfake voice calls targeting executives (CEO fraud, BEC attacks)
- Hyper-personalized phishing emails generated using NLP
- Automated social profiling from public data for planned attacks
Learn About The Rising Threat of AI-Powered Phishing: What it is, How to Detect it, and How to Prevent it Here
2. Automated Vulnerability Discovery
Attackers use AI to:
- Scan systems for security misconfigurations
- Identify zero-day vulnerabilities
- Prioritize exploits based on success probability
The attackers use these strategies to analyze and plan a swift strike with reduced time between vulnerability discovery and exploitation.
3. Malware That Learns and Adapts
AI-powered malware can:
- Change signatures to evade detection
- Learn from failed attacks
- Hide inside legitimate processes (fileless malware)
These “smart malware” variants are more difficult to detect using traditional tools.
4. AI-Generated Deepfakes and Identity Attacks
Cybercriminals create:
- Deepfake videos to spread misinformation
- Synthetic identities for financial fraud
- Fake biometric data to bypass authentication
Deepfake-as-a-service platforms have emerged on the dark web.
5. Large-Scale Botnet Automation
AI improves botnet capabilities through:
Autonomous command-and-control decision-making
- Faster DDoS adaptation based on target defenses
- Automated credential stuffing
This has led to a rise in AI-powered DDoS extortion campaigns.
How AI Is Used in Defending Against Cybercrime in 2026 (Defensive Strategy)
As offensive AI evolves, defensive AI has equally grown advanced and resilient. In 2026, AI-powered cybersecurity systems form the backbone of modern cyber defense strategies across US enterprises and government agencies. There is a widespread adoption of AI technology to strengthen the defense mechanism and cybersecurity of an organization.
Top AI-Driven Defensive Capabilities
1. Threat Detection and Prediction
AI analyzes:
- Network logs
- User behavior
- Endpoint telemetry
- Cloud traffic
- Email data
Using this data, technology helps identify anomalies, flags any potential risks, and predicts any potential attacks before they occur.
2. Autonomous Response Systems
Security automation platforms use AI technology to smartly automate systems and processes to:
- Isolate compromised endpoints
- Block malicious IPs
- Kill suspicious processes
- Trigger MFA challenges
- Roll back unauthorized changes
These responses occur in seconds, reducing mean time to respond (MTTR) which is crucial in a scenario of an attack.
3. AI-Enhanced SOC Operations
AI assists Security Operations Centers by:
- Prioritizing alerts
- Reducing false positives
- Correlating attack signals
- Providing real-time forensic insights
Such crucial data and system processes help SOC teams operate efficiently, bridging the talent shortage gap.
4. Identity Security and Behavioral Analytics
The User and Entity Behavior Analytics (UEBA) cybersecurity tool, powered by AI, identifies:
- Insider threats
- Account takeovers
- Lateral movement
- Privilege escalation attempts
Modern security calls for behavior-based detection, which is essential for building an effective zero-trust security.
5. Email Security and Phishing Prevention
AI scans emails to identify:
- Suspicious language cues
- Malicious links
- Spoofed domains
- Fraudulent attachments
This helps in significantly preventing phishing attacks and reducing the success rates of cybercrimes.
What Are the Benefits of AI in Cybersecurity in 2026
Implementing AI-powered security provides both strategic and operational benefits for organizations.
Top Benefits of AI in Cybersecurity
1. Faster Threat Detection
AI identifies threats in near real-time, reducing the time attackers remain undetected or untraced.
2. Greater Accuracy
Machine learning reduces the number of false alarms by detecting the anomalies that truly matter. This enhances the efficiency of the SOC team.
3. Reduced Human Workload
Automation handles routine tasks, allowing analysts to focus on high-impact investigations that truly matter.
4. Proactive Cyber Defense
Predictive analytics help prevent potential attacks before they occur and escalate.
5. Stronger Zero-Trust Implementation
AI continuously evaluates identities, behaviors, and access requests.
6. Improved Incident Response
Autonomous systems execute containment actions within seconds—faster than any human team.
7. Enhanced Protection Against Evasive Threats
AI catches polymorphic malware, insider threats, and unknown exploits.
8. Cost Savings
Lower breach costs, reduced downtime, and higher operational efficiency drive measurable ROI.
Top AI-Powered Cybersecurity Tools in 2026
In 2026, AI-powered cybersecurity tools will play a crucial role in detecting unknown attacks, analyzing massive volumes of security data, and responding to incidents in real time. By leveraging machine learning, behavioral analytics, and automation, these tools enable organizations to proactively defend against modern cyber risks, including endpoints, networks, cloud environments, and user identities.
Below are the leading AI cybersecurity tools and platforms widely used by US organizations in 2026:
1. Endpoint Detection & Response (EDR)
These tools run on user devices (laptops, servers, and mobile devices) to detect and stop threats, such as malware, ransomware, and unknown attacks, using AI models rather than just signatures. They can automatically analyze behavior and respond in real time.
Examples:
- CrowdStrike Falcon – AI/ML engine analyzes endpoint behavior and cloud telemetry to block malware and emerging threats.
- Sentinel One Singularity – Autonomous detection + remediation with rollback options for ransomware.
- Sophos Intercept X – Deep learning-based detection for unknown threats.
2. Network Traffic Analysis (NTA) & Intrusion Detection
These tools use AI to scan and understand patterns in network traffic. Unlike traditional tools, they spot anomalies or sophisticated threats across network flows and cloud environments.
Examples:
- Darktrace – Uses machine learning to model normal network behavior and detect deviations in real time.
- Vectra AI – AI-driven detection of lateral movement and hidden attacks.
3. Security Information & Event Management (SIEM) + UEBA
AI enhances SIEM systems by correlating millions of logs, reducing false positives, and pinpointing high-risk activity. UEBA (User & Entity Behavior Analytics) models identify unusual user behavior indicating insider threats or compromised accounts.
Examples:
- IBM QRadar AI – AI-enhanced event correlation and threat prioritization for SOC teams.
- Splunk UBA / SIEM – ML models analyze behavior across users and devices.
- Exabeam Security Management Platform – Behavioral analytics with automated workflows.
4. Extended Detection & Response (XDR) / Cloud AI Defense
XDR platforms unify signals from endpoints, networks, cloud, identity, and applications. AI interprets this massive data to detect complex attacks, automate responses, and reduce alert fatigue.
Examples:
- Palo Alto Networks Cortex XDR / XSIAM – Unified threat detection with AI orchestration.
- Microsoft Defender for Endpoint & Security Copilot AI agents – Uses AI across identity, endpoint, cloud, and assistive agents to help triage threats.
5. Phishing Detection & Email Protection
AI tools scan email content and metadata to detect phishing, spear-phishing, and harmful attachments by analyzing patterns and linguistic cues that traditional filters would miss.
Examples / Concepts:
- AI-enabled email security platforms (e.g., integrated with Microsoft Defender or standalone phishing filters).
- Research tools like AdaPhish – AI models for adaptive phishing detection and analysis using NLP.
6. Deepfake / Identity & Biometric Security
AI tools help detect synthetic media (deepfake video/audio/images) and reinforce identity verification with AI-powered biometrics. These defenses help reduce the risk of fraud and impersonation.
Examples:
- Vastav.AI – AI-based deepfake detection for audio and video authenticity checks.
7. Automation & Incident Response (SOAR)
Security Orchestration, Automation, and Response (SOAR) platforms utilize AI to coordinate multiple tools, automate workflows, and expedite response tasks, including containment, investigation, and reporting.
Capabilities:
- Automated playbooks for known threat scenarios.
- AI-assisted triage to prioritize alerts and recommend response steps.
Future of AI in Cybersecurity 2026 And Beyond
The future of AI in cybersecurity will be defined by the convergence, automation, and collaboration of the technology across ecosystems.
Key Trends Shaping the Future
1. AI-First Security Architectures
Companies will design cybersecurity systems around AI as the central component for responding to attacks and securing systems.
2. Fully Automated SOC systems
The Security Operations Centers will increasingly rely on AI for:
- Alert triage
- Investigations
- Forensics
- Automated threat hunting
AI won’t replace analysts, but it will significantly augment them. The integration of the technology will enhance the accuracy and efficiency of the SOC team.
3. AI-Driven Zero-Trust Security
AI-powered Zero Trust frameworks will be the modern security systems that will strengthen the defense systems and build cyber resilience. Real-time identity verification will rely heavily on AI-powered behavioral analytics.
4. Greater Use of Generative AI
Defenders will use gen-AI for:
- Automated reporting
- Decrypting malware
- Generating threat intelligence
While we witness an enhanced trend in cyber defense, attackers will also be weaponizing genAI to orchestrate sophisticated cyberattacks.
5. Regulatory Expansion
Expect more US federal and state mandates requiring AI-based monitoring—especially in critical infrastructure.
6. Quantum-Aware AI Security Models
As quantum computing advances, AI-driven encryption prediction and quantum-resistant algorithms will become crucial.
How Businesses Can Adopt and Adapt to AI Technology in 2026
Key Steps Businesses Must Consider in 2026
1. Conduct an AI Readiness Assessment
Integration of AI requires careful assessment and analysis before implementing the technology. Organizations must review:
- Current security posture
- Data maturity
- Cloud infrastructure
- Tool interoperability
The assessment process helps determine whether the current infrastructure can adapt to the integration of AI solutions.
2. Start with High-Impact Use Cases
Integration of AI into the current systems and infrastructure should be a planned and phased approach. Organizations must carefully evaluate and integrate security tools and technology for
- AI-powered email security
- Endpoint detection and response
- Behavioral analytics
- Automated incident response
Such security implementations tend to deliver immediate ROI if executed well.
3. Integrate AI into the Zero-Trust Framework
Use AI for:
- Continuous authentication
- Access decisioning
- Privilege monitoring
This helps strengthen the identity security within systems and safeguards access to sensitive data.
4. Upskill Cybersecurity Teams
As professionals, constantly upskilling yourself is essential to stay relevant and updated with the current industry trends and technology, especially in a rapidly evolving threat landscape. The training is essential in:
- Managing AI systems
- Interpreting AI outputs
- Responsible use of AI
- Prompt engineering for genAI-based tools
In the US, enterprises are increasingly investing in AI training and cybersecurity programs and certifications. Employers are also seeking cybersecurity professionals who are proficient with the latest tools and technologies powered by AI.
5. Establish AI Governance and Ethical Controls
Define:
- Data privacy compliance
- Bias detection mechanisms
- Model transparency
- Responsible use policies
It helps prevent misuse and reinforces trust.
6. Choose the Right AI Cybersecurity Vendors
Integration of AI technology within your IT Infrastructure isn’t as easy as it seems. This needs careful evaluation and consideration of the technology, the vendors, and the system in use. Evaluate vendors based on:
- System and Technology compatibility
- AI Model accuracy
- Integration ease
- Real-time response capabilities
- Cloud compatibility
- US compliance requirements (HIPAA, NIST, CISA, PCI DSS)
7. Continuously Monitor and Optimize AI Performance
AI systems improve data analysis, security processes, and response significantly. However, this requires constant monitoring and an ongoing process of fine-tuning to ensure that the detection accuracy stays high.
AI as the Cornerstone of Cyber Resilience in 2026 and Beyond
In 2026, AI stands at the center of both cybersecurity innovation and the evolution of cybercrime. While attackers are leveraging AI to scale and personalize their attacks, defenders are using AI to anticipate threats, automate response, and stay ahead of adversaries.
For U.S. businesses, adopting AI in cybersecurity is no longer optional—it is foundational to cyber resilience, regulatory alignment, and long-term digital trust. Organizations that integrate AI-driven security strategies today will be better equipped for the next decade of cyber challenges, where speed, intelligence, and automation define the difference between vulnerability and security.
Preparing the next generation of cybersecurity leaders is equally critical. EC-Council University’s Master of Science in Computer Science degree program is uniquely positioned to meet this demand, with a curriculum enriched by cybersecurity, artificial intelligence, blockchain, and robotics. As a cybersecurity-focused university, EC-Council University equips students with comprehensive, hands-on expertise in these cutting-edge domains—empowering graduates to lead, innovate, and protect digital ecosystems at the forefront of global cybersecurity advancements.







